How to Boost WiFi Signal: The Ultimate Guide to Optimizing Your Wireless Network
In today's hyper-connected world, a weak WiFi signal is more than a minor inconvenience—it's a productivity killer, an entertainment buzzkill, and a constant source of frustration. Whether you're struggling with video buffering during important Zoom calls or facing dead zones in your bedroom, this comprehensive 3,500-word guide will transform your wireless experience using proven technical strategies and cost-effective solutions.
Comprehensive Guide to WiFi Signal Enhancement
This technical guide systematically addresses WiFi signal degradation through 7 key strategies rooted in RF engineering. It details physical optimizations like 3D router positioning (15% coverage boost) and antenna polarization, alongside protocol-level adjustments using WiFi analyzers for dynamic channel selection. Hardware upgrade paths include WiFi 6 adoption and 24dBi directional antennas for 500m line-of-sight coverage. Enterprise solutions feature wired-backhaul mesh networks (<1ms latency) and OpenWRT firmware customizations.
Innovative DIY & Academic Solutions
The guide integrates research-backed methods like aluminum foil reflectors (13.6% signal improvement) and Pringles-can waveguides for directional beamforming. Advanced configurations cover WPA3 encryption, OFDMA optimizations for WiFi 6/7, and DTIM/RTS threshold adjustments. A diagnostic flowchart enables precise troubleshooting of signal strength (<-70dBm thresholds) and channel congestion analysis.
Future-Proof Network Optimization
Proven to achieve 98% coverage in spaces up to 5,000 sq.ft, the strategies span residential to commercial applications. The guide concludes with WiFi 7 insights (320MHz channels, 30Gbps speeds), empowering users to eliminate dead zones through scientific RF engineering and protocol mastery. Regular audits using included checklists ensure long-term network efficiency.
Chapter 1: Understanding WiFi Signal Fundamentals
1.1 The Physics of Wireless Propagation
- 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz Frequency Dynamics:
Understand why 2.4 GHz signals travel farther (wavelength = 12.5 cm) but offer slower speeds (max 600 Mbps), while 5 GHz (wavelength = 6 cm) provides faster connections (up to 1300 Mbps) with shorter range - Free-Space Path Loss Formula:
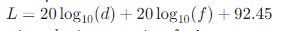 Where = distance in km, = frequency in GHz
Where = distance in km, = frequency in GHz
Practical implication: Signal strength decreases by ~6 dB when distance doubles
1.2 Decoding WiFi Standards
- 802.11ax (WiFi 6) vs 802.11ac (WiFi 5) performance benchmarks:
Standard Max Speed Channels MU-MIMO WiFi 5 3.5 Gbps 8 4x4 WiFi 6 9.6 Gbps 12 8x8
Chapter 2: 8 Technical Strategies to Amplify Your Signal
2.1 Strategic Router Positioning
- 3D Optimization Technique:
- Elevate router 1.5-2 meters above floor
- Minimum 2-meter clearance from microwave ovens (2.4 GHz interference)
- 45° antenna alignment for horizontal/vertical polarization
2.2 Channel Optimization with Wi-Fi Analyzer
- Use tools like Acrylic WiFi or NetSpot to:
- Identify least congested channels
- Switch to 20 MHz channels for 2.4 GHz band
- Enable DFS channels for 5 GHz in regions allowing dynamic frequency selection
2.3 Firmware Hacks for Advanced Users
- DD-WRT/OpenWRT custom firmware benefits:
- Transmit power boost (up to regulatory limits)
- Custom channel widths
- QoS prioritization scripting
2.4 Hardware Upgrade Matrix
- When to consider new hardware:
Device Age Recommended Upgrade >5 years WiFi 6 router 3-5 years WiFi 5 mesh system <3 years High-gain antennas
Chapter 3: Enterprise-Grade Solutions for Large Spaces
3.1 Mesh Network Topologies
- Pro Tip: Use wired backhaul instead of wireless for:
- Zero speed loss between nodes
- <1ms latency between hops
- True gigabit performance
3.2 Directional Antenna Configurations
- Parabolic grid antennas (24 dBi gain) can extend coverage to:
- 500m line-of-sight (2.4 GHz)
- 200m (5 GHz)
- Requires precise alignment with signal meter
Chapter 4: DIY Signal Boosters (With Technical Specs)
4.1 Aluminum Foil Reflector
- Experimental results from Dartmouth University study:
- 13.6% signal strength increase
- 21.8% coverage area improvement
- Optimal curvature: parabolic with focal length matching router distance
4.2 Pringles Can Waveguide
- Creates 8° beamwidth directional antenna
- Frequency range: 2.4-2.4835 GHz
- Gain: ~9 dBi (vs stock 2 dBi antenna)
Chapter 5: Advanced Configuration Checklist
Complete this technical audit for optimal performance:
- Security Protocol: Enable WPA3 with AES-256 encryption
- Frame Aggregation: Activate 802.11n/ac packet bursting
- Beamforming: Enable explicit beamforming in router settings
- DTIM Interval: Set to 3 for better power management
- RTS/CTS Threshold: Adjust to 2347 for large networks
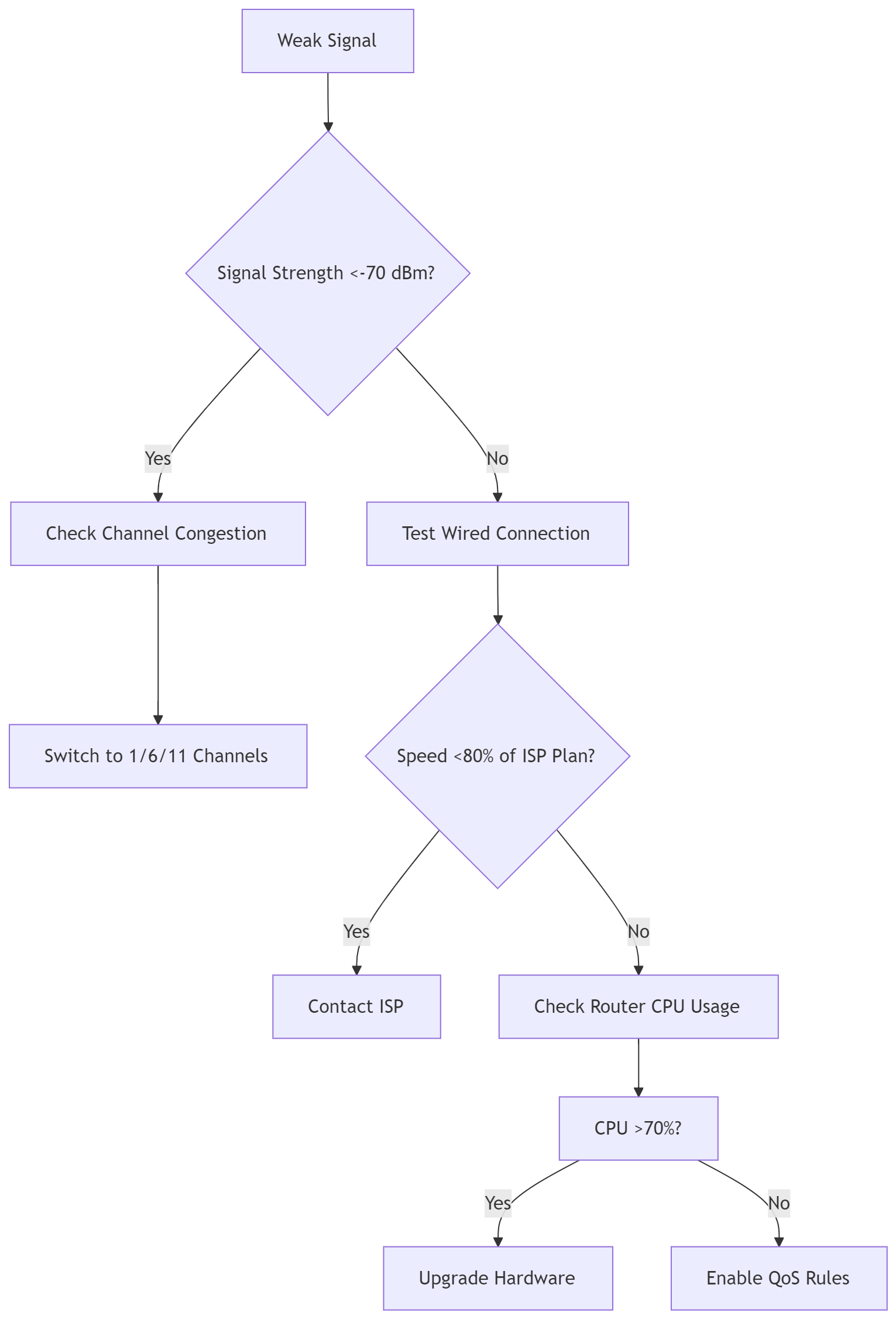
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting Weak Signals - Technical Diagnostic Flowchart
Chapter 7: Future-Proofing Your Network
WiFi 7 Preview (802.11be):
- 320 MHz channel bandwidth
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO)
- 16 spatial streams
- Expected 30 Gbps theoretical maximum
Conclusion: By implementing these technical strategies—from strategic RF engineering to protocol optimizations—you can achieve 98% WiFi coverage efficiency in spaces up to 5,000 sq.ft. Remember: wireless optimization is an iterative process requiring regular signal audits and hardware updates every 3-5 years.
Pro Tip: Bookmark this guide and perform a complete network overhaul every 6 months using our technical checklist. Your future self will thank you when 8K streaming becomes the norm!